
Dec . 23, 2024 05:24 Back to list
Understanding and Preventing Corrosion in Steam Boiler Systems for Enhanced Longevity and Efficiency
Understanding Corrosion in Steam Boilers Causes, Consequences, and Prevention
Corrosion in steam boilers is a critical issue that impacts the efficiency, safety, and longevity of these essential industrial components. Steam boilers are used in various applications, from power generation to food processing and chemical manufacturing, making their reliability crucial. However, the presence of corrosive elements can lead to significant problems if not properly managed. This article will explore the causes, consequences, and prevention methods related to corrosion in steam boilers.
Causes of Corrosion
Corrosion in steam boilers primarily arises from water chemistry, operational conditions, and materials used in construction. The following factors are pivotal in understanding the root causes of corrosion
1. Water Quality The quality of the water used in steam generation significantly influences corrosion rates. High levels of dissolved oxygen, carbon dioxide, and chloride ions can accelerate corrosion. For instance, oxygen can contribute to pitting and localized corrosion, while chloride ions can lead to stress corrosion cracking.
2. Temperature and Pressure High temperatures and pressures exacerbate the corrosive effects of water and steam. Elevated temperatures can increase the solubility of corrosive species, enhancing their reactivity with boiler materials.
3. Material Selection The materials used in steam boiler construction play a crucial role in corrosion susceptibility. Carbon steels, while cost-effective, are highly prone to corrosion. Stainless steels and other alloyed materials offer better resistance but may still succumb to specific types of corrosion in certain environments.
4. Operational Practices Inadequate boiler maintenance and improper operational practices can also lead to corrosion. For example, insufficient blowdown can result in the accumulation of harmful impurities in the boiler water.
Consequences of Corrosion
The impact of corrosion on steam boilers can be both direct and indirect, with serious implications for industrial operations
1. Reduced Efficiency Corrosion can create scale and deposits on heat transfer surfaces, leading to reduced thermal efficiency. This results in higher fuel consumption and operational costs.
steam boiler corrosion
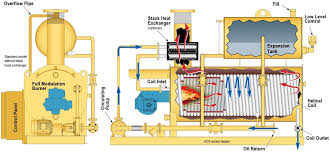
2. Equipment Damage Prolonged corrosion can cause significant damage to boiler components. For instance, the failure of pressure vessels or pipes can lead to leaks, downtimes, and even catastrophic failures, posing safety risks to personnel.
3. Increased Maintenance Costs Regular maintenance and repairs become necessary as corrosion progresses. The costs associated with these repairs can be substantial, impacting the overall operational budget.
4. Safety Hazards Corrosion-related failures can pose serious safety hazards, including explosions due to sudden pressure relief or the release of hazardous materials. Ensuring boiler integrity is paramount to sustaining safe working conditions.
Prevention and Mitigation Strategies
To manage corrosion effectively, industries must adopt proactive measures. Here are some key strategies for preventing corrosion in steam boilers
1. Water Treatment Implementing comprehensive water treatment protocols is essential. This may include deoxygenation methods, pH control, and the use of corrosion inhibitors. Monitoring water chemistry regularly helps to maintain optimal conditions.
2. Material Selection and Coating Choosing corrosion-resistant materials and applying protective coatings can greatly enhance the lifespan of steam boiler components. Options such as stainless steel, alloy steel, and ceramic coatings should be considered based on specific operating conditions.
3. Regular Inspections and Maintenance Conducting routine inspections to identify early signs of corrosion is crucial. Maintenance programs should include blowdown procedures, cleaning of boiler tubes, and replacement of any deteriorated components.
4. Training and Awareness Educating personnel about the causes and consequences of corrosion, as well as proper operational practices, fosters a culture of safety and reliability. Enhanced awareness can lead to better decision-making and incident prevention.
Conclusion
Corrosion in steam boilers poses significant challenges that can affect operational efficiency and safety. By understanding its causes and consequences, and implementing effective prevention strategies, industries can mitigate the risks associated with this pervasive issue. It is essential for operations to prioritize water quality, select appropriate materials, and conduct regular maintenance to ensure the longevity and safety of their steam boilers. With proactive measures in place, industries can enhance performance, reduce costs, and protect their workforce from the dangers of corrosion.
-
High-Efficiency Commercial Oil Fired Steam Boiler for Industry
NewsJul.30,2025
-
High-Efficiency Biomass Fired Thermal Oil Boiler Solutions
NewsJul.30,2025
-
High Efficiency Gas Fired Thermal Oil Boiler for Industrial Heating
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Efficiency Gas Fired Hot Water Boiler for Sale – Reliable & Affordable
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High Efficiency Biomass Fired Hot Water Boiler for Industrial and Commercial Use
NewsJul.29,2025
-
High-Efficiency Biomass Fired Hot Water Boiler for Industrial Use
NewsJul.28,2025
Related PRODUCTS






















